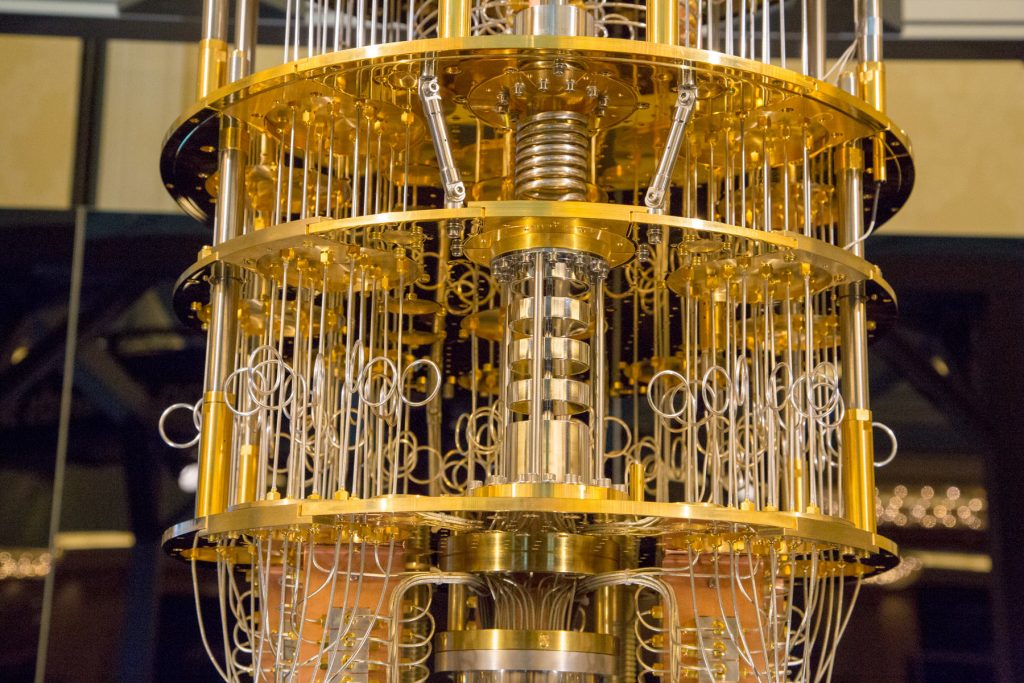
Quantum computing is revolutionizing the way we approach computation, promising unprecedented processing power that could redefine industries ranging from cryptography and artificial intelligence to drug discovery and materials science. Unlike classical computers that rely on binary bits (0s and 1s), quantum computers operate using quantum bits, or qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously due to the principles of superposition and entanglement. Over the past few years, significant strides have been made in the field of quantum computing, bringing us closer to harnessing its full potential.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Quantum Computing
Classical computers process data sequentially, with each bit representing either a 0 or a 1. In contrast, quantum computers leverage the unique properties of qubits to perform multiple calculations at once. This capability arises from two key quantum mechanical phenomena:
- Superposition: Qubits can exist in a combination of both 0 and 1 states at the same time, exponentially increasing the computational power.
- Entanglement: When qubits become entangled, the state of one qubit is instantly correlated with the state of another, regardless of distance. This feature enables faster and more efficient processing compared to classical computers.
By utilizing these principles, quantum computers can solve complex problems much faster than traditional systems, making them ideal for applications requiring high computational power.
Recent Breakthroughs in Quantum Computing
1. Achieving Quantum Supremacy
One of the most significant milestones in quantum computing was Google’s claim in 2019 of having achieved “quantum supremacy.” Google’s quantum processor, Sycamore, reportedly completed a task in 200 seconds that would have taken the most advanced supercomputer 10,000 years to finish. While this claim sparked debate, it demonstrated the feasibility of quantum computing outperforming classical machines in specific tasks.
2. Advancements in Qubit Stability and Error Correction
One of the biggest challenges in quantum computing has been qubit instability and high error rates due to environmental interference. Researchers have been making significant progress in developing error correction techniques that improve the reliability of quantum computations. In 2023, IBM announced its new error-correcting quantum algorithm, which enhances qubit fidelity and reduces noise, bringing us one step closer to practical quantum applications.
3. Superconducting Qubits and Topological Qubits
Quantum computing hardware has seen significant improvements, with superconducting qubits being the most widely used approach. Companies like Google, IBM, and Rigetti Computing are actively refining this technology. Meanwhile, Microsoft is investing in topological qubits, which promise greater stability and error resistance, potentially leading to more scalable quantum systems.
4. Quantum Networking and the Quantum Internet
Another emerging area of development is quantum networking, which aims to create a secure quantum internet. China has been a frontrunner in this field, successfully demonstrating quantum communication over long distances through satellite-based quantum key distribution (QKD). This advancement could lead to ultra-secure communication networks resistant to cyberattacks.
5. Hybrid Quantum-Classical Computing
Recognizing the current limitations of quantum technology, researchers are exploring hybrid quantum-classical computing models. Companies like IBM and Amazon Web Services (AWS) are developing cloud-based quantum computing platforms that integrate classical and quantum processors, enabling users to leverage quantum power for specific tasks while relying on classical computing for others.
Applications of Quantum Computing
1. Cryptography and Cybersecurity
Quantum computing poses both a threat and an opportunity for cybersecurity. While it could potentially break traditional encryption algorithms, it also paves the way for quantum cryptography techniques like quantum key distribution (QKD), which offers unparalleled security.
2. Drug Discovery and Molecular Simulation
Quantum computing is expected to revolutionize drug discovery by simulating complex molecular structures with high accuracy. Pharmaceutical companies, including Pfizer and Roche, are investing in quantum research to accelerate the development of new drugs and treatments.
3. Financial Modeling and Optimization
Financial institutions are exploring quantum computing for portfolio optimization, risk assessment, and fraud detection. Quantum algorithms could analyze massive datasets more efficiently than traditional computing, enabling better decision-making in financial markets.
4. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Quantum machine learning has the potential to enhance AI capabilities by processing vast amounts of data at unprecedented speeds. Companies like Google and IBM are working on quantum algorithms that could improve pattern recognition, optimization, and natural language processing.
5. Climate Modeling and Energy Solutions
Quantum computing could help tackle climate change by optimizing energy use and improving climate models. Quantum simulations can provide insights into material properties, aiding in the development of better batteries and renewable energy technologies.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Despite rapid advancements, quantum computing still faces several challenges:
- Scalability: Current quantum computers are limited in the number of qubits they can reliably use. Achieving large-scale quantum computing requires breakthroughs in qubit stability and connectivity.
- Error Rates: Quantum computations are prone to errors due to environmental factors like temperature fluctuations and electromagnetic interference. Researchers are continuously developing error-correction techniques to improve reliability.
- High Costs and Infrastructure Requirements: Quantum computers require extreme conditions, such as near-absolute zero temperatures, making them expensive and challenging to maintain.
- Software and Algorithm Development: The field lacks a standardized programming approach, and more work is needed to create quantum algorithms that can be easily integrated into practical applications.
Conclusion
Quantum computing is at the forefront of technological innovation, promising to revolutionize industries and solve problems beyond the capabilities of classical computers. With significant investments from tech giants and government agencies worldwide, quantum computing is inching closer to practical applications. While challenges remain, ongoing research and collaboration are expected to drive further breakthroughs, paving the way for a new era of computing. As we continue to explore the possibilities of quantum mechanics, the future of computation looks incredibly promising, with the potential to transform industries and scientific discovery in ways we have yet to imagine.
Written by Abrar Sayeed